News
Expert insight: all you need to know about ship certification
Published
01 July 2025
Ship certifications are fundamental to ensuring that commercial vessels operate safely, comply with international and regional maritime regulations, and contribute to global sustainability goals.
From structural integrity to emissions management and crew competence, ship certifications provide documented proof that vessels meet specific legal, technical, and environmental standards. In this article, we delve into the complex certification landscape, focusing on regulatory frameworks, wind-assisted propulsion systems (WAPS), and the role of classification societies.
International and regional regulations governing ship certifications
At the global level, ship certifications are anchored in key conventions developed by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). These include:
- SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea, 1974): Establishes minimum safety standards for ship construction, equipment, and operational procedures.
- MARPOL (1973/78): Regulates pollution from ships. Annex VI is particularly relevant for air emissions, including sulphur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and metrics like EEDI and EEXI.
- STCW Convention: Ensures seafarers are trained and certified to international competency standards.
- ISM Code: Integrated into SOLAS Chapter IX, mandates Safety Management Systems to prevent human injury and environmental damage.
- COLREG: Defines collision prevention rules.
- MLC (2006): Adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO), sets minimum working and living standards for seafarers.
Additional conventions include the Load Line Convention, IMSBC Code, and Ballast Water Management (BWM) Convention.
At the regional level, the European Union enforces:
- MRV Regulation (2015/757): Requires CO₂ monitoring and reporting.
- EU ETS (2024): Includes maritime shipping in the emissions trading system.
- FuelEU Maritime (2025): Mandates reductions in the greenhouse gas (GHG) intensity of fuels.
These regulations directly influence ship certifications, requiring both documentary evidence and technical compliance measures. National maritime authorities are responsible for transposing these standards into domestic law and enforcing them via inspections and audits.
Regulatory framework for Wind-Assisted Propulsion Systems (WAPS) and ship certifications
Wind-assisted propulsion systems (WAPS) are emerging as viable energy-efficiency technologies for maritime decarbonization. Their integration into vessels is supported by evolving certification pathways:
- IMO Guidelines (MEPC.1/Circ.896, 2021): Permit WAPS contributions to EEDI/EEXI compliance calculations.
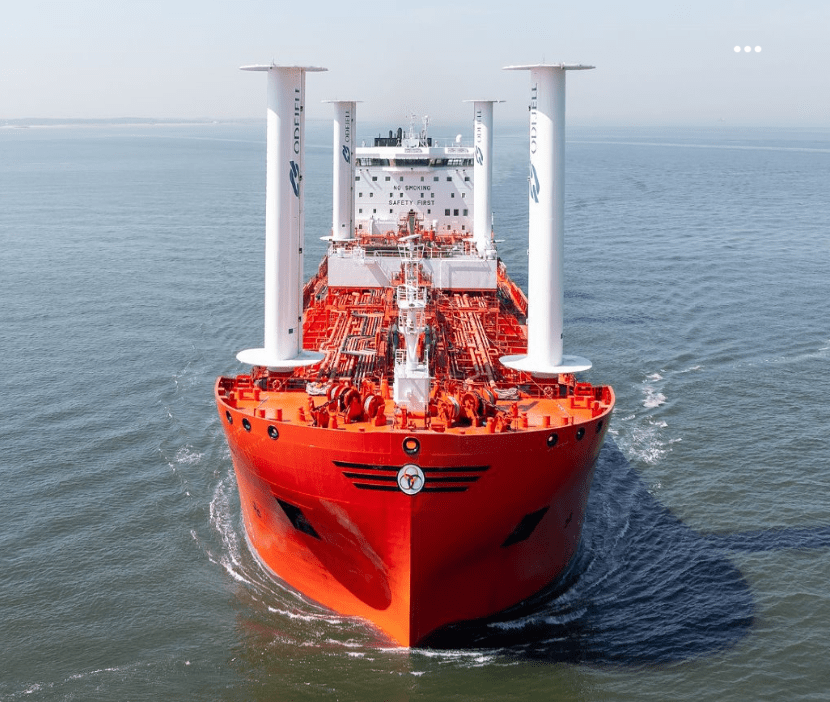
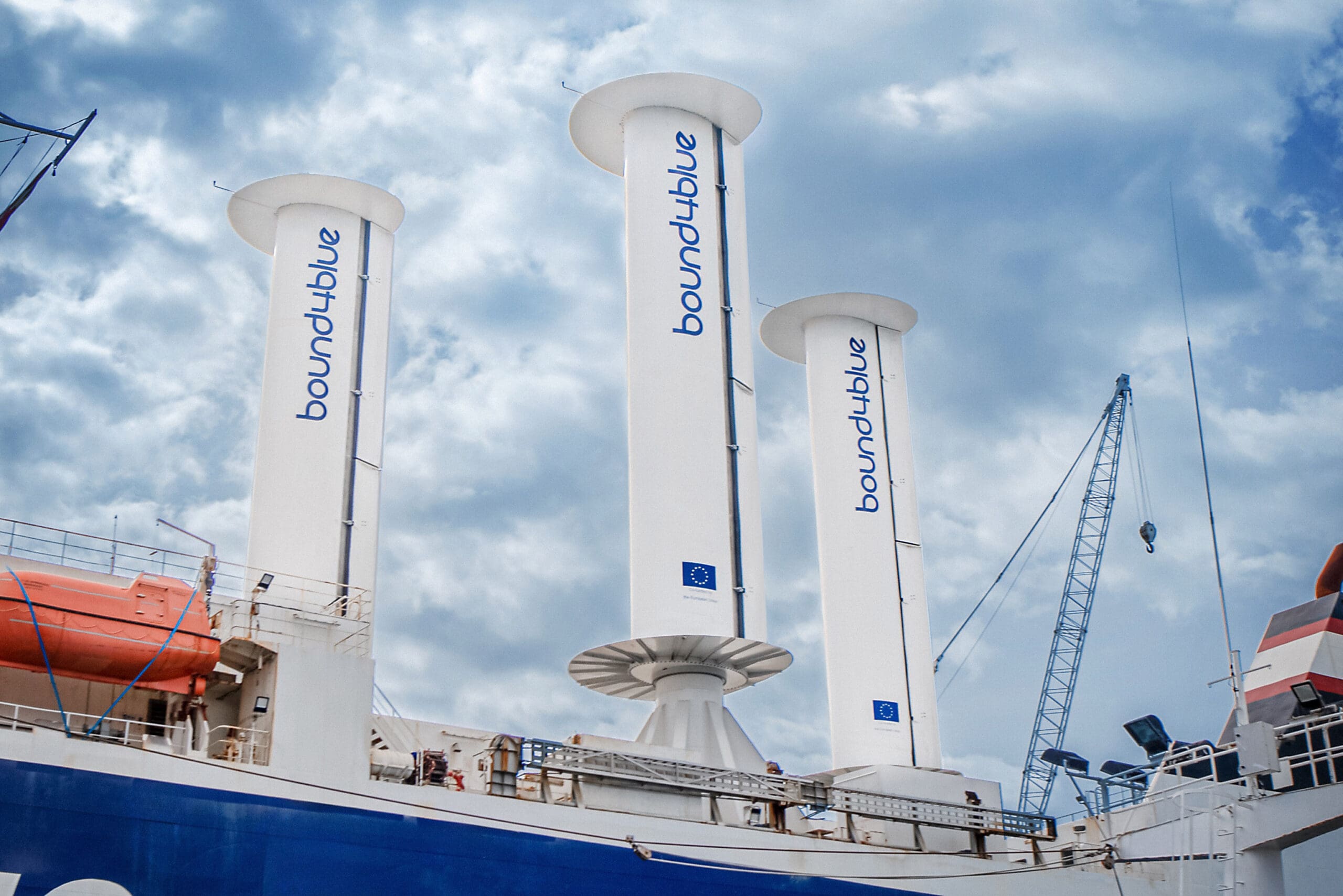
- Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) compliance: WAPS, such as bound4blue’s eSAIL® technology, offer significant advantages under the IMO’s CII framework, which rates vessels from A (best) to E (worst) based on annual CO₂ emissions per cargo mile
- Updated EEDI/EEXI Formulas (2022): Enable more accurate performance reflection for WAPS.
- EU Green Regulations: WAPS contribute positively to FuelEU Maritime and EU ETS compliance.
Despite their innovation, WAPS installations must comply with existing and newbuilds ship safety and design requirements, including International regulations provisions on structural integrity, visibility, maneuverability, among others. This often necessitates:
- Integration project: The integration of WAPS often requires a dedicated project to assess their impact on key design parameters such as structural integrity, stability, and bridge visibility. These aspects should be reviewed by qualified professionals – including naval architects or experienced technical offices -either as part of a formal integration project or within the shipyard or owner’s engineering team. This ensures that the installation meets all applicable safety and operational standards before classification and certification processes begin.
- Supplementary ship certifications and classification approval
Shipowners deploying WAPS should engage early with classification societies and flag states to define certification pathways and ensure uninterrupted regulatory compliance.
Classification societies and technical ship certifications for WAPS
At bound4blue, we work closely with all major classification societies to ensure that our eSAIL® technology meets the highest safety, structural, and performance standards. We’ve collaborated hand-in-hand with DNV, Bureau Veritas, ABS, Lloyd’s Register, and ClassNK – not only to secure the required certifications, but also to successfully install eSAIL® systems on vessels classed under each of them. This ongoing collaboration ensures regulatory alignment and paves the way for the seamless integration of wind-assisted propulsion across diverse fleets.
- DNV
- ST-0511 Standard: Governs structural loads and safety criteria for wind propulsion.
- WAPS Notation: Covers integration, control systems, electricals, and compliance with statutory standards.
- Approval in Principle (AIP) and Type Approval processes validate new WAPS designs: granted during SMM Hamburg 2024, this Type Approval by DNV certifies the design safety and quality of eSAIL® systems, accelerating their adoption in commercial fleets.
- Bureau Veritas (BV)
- NR 206 Guidelines: Applicable to all wind technologies (sails, Flettner rotors, kites).
- WPS-1 and WPS-2 Notations: Require risk analysis (e.g., HAZID) and operational documentation.
- American Bureau of Shipping (ABS)
- WAPS Installation Guide (2020): Covers rigid sails, Flettner rotors, and safety integration.
- Lloyd’s Register (LR)
- LR-GN-044 (2024): Establishes construction rules, structural verifications, and integrity assessment for WAPS.
- ClassNK
- 2019 Guidelines: Provide structural verification methods and class notations.
These classification standards ensure WAPS meet performance, safety, and compliance metrics. They also standarize the process of obtaining the necessary ship certifications required for both operation and regulatory alignment.
The strategic role of ship certifications in maritime innovation
Ship certifications are no longer passive compliance documents; they are strategic enablers for clean technology adoption. For example, wind propulsion systems like bound4blue’s eSAIL® technology are designed not only to reduce emissions and fuel consumption but also to align with current and future certification standards.
By meeting all relevant statutory and voluntary ship certifications – including SOLAS, MARPOL, EEXI, and class-specific notations – eSAIL® ensures seamless regulatory compliance. Moreover, company’s certifications such as ISO 9001, 14001, and 50001 reinforce a company’s leadership in sustainable shipping.
Conclusion: why ship certifications matter more than ever
In today’s decarbonizing maritime industry, ship certifications are a cornerstone of operational readiness, competitive edge, and environmental stewardship. Whether mandated by IMO conventions, regional regulations, or technical standards from classification societies, ship certifications facilitate trust, safety, and transparency.
With the growing integration of innovative solutions like WAPS, and the tightening of emissions-related frameworks such as the EU ETS and FuelEU Maritime, the role of ship certifications is only set to increase. Companies that stay ahead in compliance will also lead in sustainability.
To find out more about why wind is the ultimate complementary solution for alternative fuels, please contact us enquiries@bound4blue.com.